Spis treści
The XTT^2 ALSV(FD) Specification
Author: Grzegorz J. Nalepa, based on the work with Antoni Ligęza
Version: Draft 2008Q3
Introduction to Attributive Logics
- Attributive logics constitute a simple yet widely-used tool for knowledge specification and development of rule-based systems.
- In fact in a large variety of applications in various areas of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Knowledge Engineering (KE) attributive languages constitute the core knowledge representation formalism.
- The most typical areas of applications include rule-based systems, expert systems (ones based on rule formalism) and advanced database and data warehouse systems with knowledge discovery applications and contemporary business rules and business intelligence components.
Introduction to Attributive Logics
The description of AL presented here is based on several papers, including
ALSV(FD)
- In SAL (Set Attributive Logic) as well as in its current version ALSV(FD), the very basic idea is that attributes can take atomic or set values.
- After (ali2005thebook) it is assumed that an attribute A_i is a function (or partial function) of the form
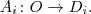 Here O is a set of objects and D_i is the domain of attribute A_i.
Here O is a set of objects and D_i is the domain of attribute A_i.
- A generalized attribute A_i is a function (or partial function) of the form
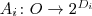 where 2^D_i is the family of all the subsets of D_i.
where 2^D_i is the family of all the subsets of D_i.
ALSV(FD)
- The basic element of the language of Attribute Logic with Set Values over Finite Domains (ALSV(FD) for short) are attribute names and attribute values.
- For simplicity of presentation no objects are considered here; in practice, the same attribute applied to two (or more) different objects can be considered as two (or more) new, different, object-labelled attributes.
- Unless two (or more) different objects are considered at the same time, no explicite reference to an object is necessary.
ALSV(FD)
- Let us consider:
- A – a finite set of attribute names,
- D – a set of possible attribute values (the domains).
- Let A = A_1, A_2, … ,A_n be all the attributes such that their values define the state of the system under consideration. It is assumed that the overall domain D is divided into n sets (disjoint or not), D = D_1 u D_2 u … u D_n, where D_i is the domain related to attribute A_i, i=1,2, … ,n.
- Any domain D_i is assumed to be a finite (discrete) set. The set can be ordered, partially ordered, or unordered; in case of ordered (partially ordered) sets some modifications of the notation are allowed.
ALSV(FD)
- As we consider dynamic systems, the values of attributes can change over time (or state of the system).
- We consider both simple attributes of the form A_i : T → D_i (i.e. taking a single value at any instant of time) and generalized ones of the form A_i: T → 2^D_i (i.e. taking a set of values at a time); here T denotes the time domain of discourse.
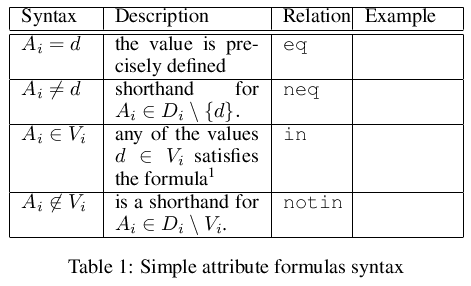
Syntax
Syntax
Syntax
- In case V_i is an empty set (the attribute takes in fact no value) we shall write A_i = ' '.
- More complex formulae can be constructed with conjunction
^(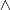 ) and disjunction
) and disjunction v; both the symbols have classical meaning and interpretation. - There is no explicit use of negation.
Syntax
- The proposed set of relations is selected for convenience and as such is not completely independent. For example, A_i = V_i can perhaps be defined as A_i \subset V_{i} ^ A_i \supset V_i; but it is much more concise and convenient to use
=directly. - Various notational conventions extending the basic notation can be used. For example, in case of domains being ordered sets, relational symbols such as >, >=, <, =< can be used with the straightforward meaning.
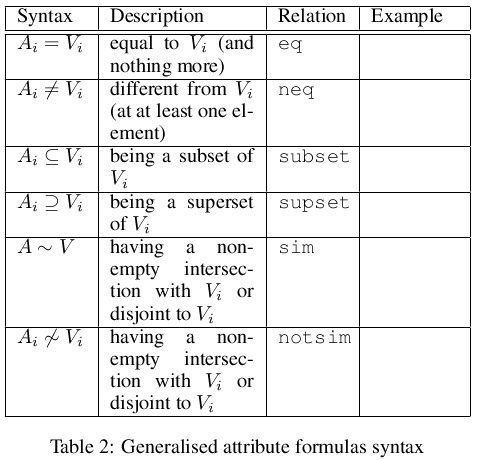
Semantics
- In SAL the semantics of A_i=d is straightforward – the attribute takes a single value.
- The semantics of A_i=t is that the attribute takes all the values of t (the so-called internal conjunction) while the semantics of A_i \in t is that it takes one (in case of simple attributes) or some (in case of generalized attributes) of the values of t (the so-called internal disjunction).
- As an example for the necessity of SAL one can consider the specification of working days (denoted with WDay) given as WDay = D, where D is the set of working days, D = { Monday,Tuesday,Wednesday,Thursday,Friday }. Now one can construct an atomic formula like CurrentDay \in D, or a rule of the form: DayOfInterest \in D → Status(OfficeOfInterest) = open.
Semantics
- The semantics of
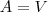 is basically the same as the one of basic SAL.
is basically the same as the one of basic SAL. - If
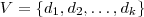 then
then 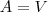 is equivalent to
is equivalent to 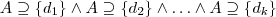 i.e. the attribute takes all the values specified with
i.e. the attribute takes all the values specified with 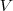 (and nothing more).
(and nothing more). - The semantics of
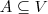 ,
, 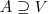 and
and 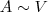 is defined as follows:
is defined as follows:  where U subset V, i.e. A takes some of the values from V (and nothing out of V),
where U subset V, i.e. A takes some of the values from V (and nothing out of V),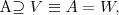 where V subset W, i.e. A takes all of the values from V (and perhaps some more),
where V subset W, i.e. A takes all of the values from V (and perhaps some more),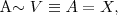 where
where 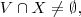 i.e. A takes some of the values from V (and perhaps some more).
i.e. A takes some of the values from V (and perhaps some more).
- As it can be seen, the semantics of ALSV is defined by means of relaxation of logic to simple set algebra.
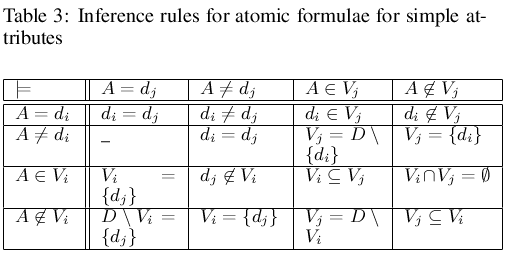
Inference Rules
- Let V and W be two sets of values such that V subset W. We have the following straightforward inference rules for atomic formulae:
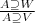 i.e. if an attribute takes all the values of a certain set it must take all the values of any subset of it (downward consistency).
i.e. if an attribute takes all the values of a certain set it must take all the values of any subset of it (downward consistency). - Similarly
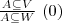 i.e. if the values of an attribute takes values located within a certain set they must also belong to any superset of it (upward consistency).
i.e. if the values of an attribute takes values located within a certain set they must also belong to any superset of it (upward consistency). - These rules seem a bit trivial, but they must be implemented for enabling inference, e.g they are used in the rule precondition checking.
Inference Rules
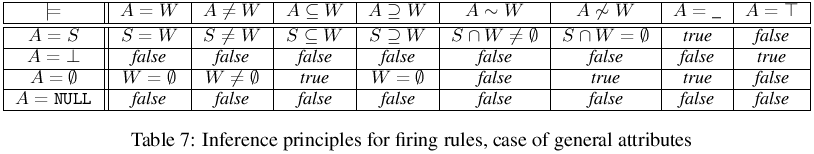
- The table is to be read as follows: if an atomic formula in the leftmost column holds, and a condition stated in the same row is true, the to appropriate atomic formula in the topmost row is a logical consequence of the one from the leftmost column.
Inference Rules
 (The rules must be checked; simple rules are for matching preconditions to the state formula. More complex rules can be for establishing truth-value propagation among atoms of preconditions within a table).
(The rules must be checked; simple rules are for matching preconditions to the state formula. More complex rules can be for establishing truth-value propagation among atoms of preconditions within a table).
![]()
![]()
![]()
Inference Rules
- In Tables 3 and 4 the conditions are satisfactory ones.
- It is important to note that in case of the first rows of the tables (the cases of A=d_i and A=V, respectively) all the conditions are also necessary ones.
- The interpretation of the tables is straightforward: if an atomic formula in the leftmost column in some row i is true, then the atomic formula in the topmost row in some column j is also true, provided that the relation indicated on intersection of row i and column j is true.
- The rules of Table 3 and Table 4 can be used for checking if preconditions of a formula hold or verifying subsumption among rules.
Inference Rules
- The interpretation of the Table 5 is straightforward: if the condition specified at the intersection of some row and column holds, then the atomic formulae labelling this row and column cannot simultaneously hold. Note however, that this is a satisfactory condition only.
- The Table can be used for analysis of determinism of the system, i.e. whether satisfaction of precondition of a rule implies that the other rules in the same table cannot be fired.
State, State Representation and Inference
- When processing information, the current values of attributes form the state of the inference process.
- The values of attributes can, in general, be modified in the following three ways:
- by an independent, external system,
- by the inference process, and
- as some clock-dependent functions.
State, State Representation and Inference
- The first case concerns attributes which represent some process variables, which are to be incorporated in the inference process, but depend only of the environment and external systems.
- As such, the variables cannot be directly influenced by the XTT system.
- Examples: external temperature, the age of a client or the set of foreign languages known by a candidate.
- Values of such variables are obtained as a result of some measurement or observation process.
- They are assumed to be put into the inference system via a blackboard communication method; in fact they are written directly into the internal memory whenever their values are obtained or changed.
State, State Representation and Inference
- The second case concerns the values of attributes obtained at certain stage of reasoning as the result of the operations performed in RHS of XTT.
- The new values of the attributes can be:
- asserted to global memory (and hence stored and made available for any components of the system), or
- kept as values of internal process variables.
State, State Representation and Inference
- The first solution is offered mostly for permanent changes; before asserting new values typically and appropriate retract operation is to be performed so as to keep a consistent state. In this way also the history (trajectory) of the system can be stored, provided that each value of an attribute is stored with a temporal index.
- The second solution is offered for value passing and calculations which do not require permanent storage. For example, if a calculated value is to be passed to some next XTT component and it is no longer used after, it is not necessary to store it in the global memory.
The State of the System
- The current state of the system is considered as a complete set of values of all the attributes in use at a certain instant of time.
- The concept of the state is similar to the one in dynamic systems and state-machines.
- The representation of the state should satisfy the following requirements:
- the specification is internally consistent,
- the specification is externally consistent,
- the specification is complete,
- the specification is deterministic,
- the specification is concise.
The State of the System
- The first postulate says that the specification itself cannot be inconsistent at the syntactic level. For example, a simple attribute (one taking a single value) cannot take two different values at the same time. In general, assuming independence of the attributes and no use of explicit negation, each value of an attribute should be specified once.
- The second postulate says, that only true knowledge (with respect to the external system) can be specified in state. In other words, facts that are syntactically correct but false cannot occur in the state formula.
The State of the System
- The third postulate says, that all the knowledge true at a certain instant of time should be represented within the state.
- The four postulate says that there can be no disjunctive knowledge specification within the state.
- Finally, the fifth postulate says that no unnecessary, dependent knowledge should be kept in the state. In databases and most of the knowledge bases this has a practical dimension: only true facts are represented explicitly.
The State of the System
- The current values of all the attributes are specified with the contents of the knowledge-base (including current sensor readings, measurements, inputs examination, etc.).
- From logical point of view it is a formula of the form:
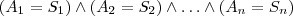 where
where 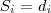 (
(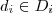 ) for simple attributes and
) for simple attributes and 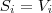 , (
, (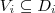 ) for complex.
) for complex.
The State of the System
- In order to cover realistic cases some explicit notation for covering unspecified, unknown values is proposed; this is so to deal with the data containing the NULL values imported from a database.
- The first case refers to unspecified value of an attribute as a consequence of inappropriateness. A formula of the form
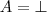 means that the attribute
means that the attribute  takes an empty set of values (no value at all) at the current instant of time (or forever) for the object under consideration.
takes an empty set of values (no value at all) at the current instant of time (or forever) for the object under consideration. - For example, the attribute
Maiden_NameorThe_Year_of_Last_Pregnancyfor a man is not applicable and hence it takes no value for all men.
The State of the System
- The second case refers to a situation that the attribute may be applied to an object, but it takes no value. This will be denoted as
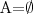 .
. - For example, the formula
Phone_Number=\emptyset means that the considered person has no phone number. - The third case is for covering the
NULLvalues present in relational databases. A formula of the form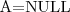 means that attribute
means that attribute 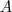 takes an unspecified value.
takes an unspecified value.
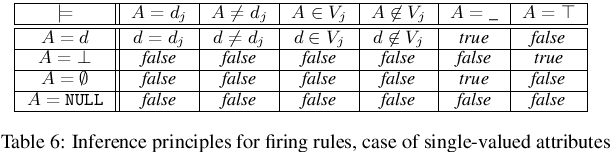
State and rule firing
- In order to fire a rule all the precondition facts defining its LHS must be true within the current state.
- The verification procedure consists in matching these fact against the state specification.
- A separate procedure concerns simple (single-valued) attributes, and a separate one is applied in case of complex attributes.
State and rule firing
State and rule firing
ALSV Rules
- ALSV(FD) has been introduced with practical applications for rule languages in mind.
- In fact, the primary aim of the presented language is to extend the notational possibilities and expressive power of the XTT-based tabular rule-based systems.
- An important extension consist in allowing for explicit specification of one of the symbols eq, neq, in, notin, subset, supset, sim, notsim, with an argument in the table.
Rule Format
Consider a set of n attributes A = A_1,A_2, …, A_n Any rule is assumed to be of the form:
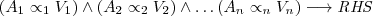 where alpha_i is one of the admissible relational symbols in ALSV(FD),
and RHS is the right-hand side of the rule covering conclusion and perhaps the retract and assert definitions if necessary.
where alpha_i is one of the admissible relational symbols in ALSV(FD),
and RHS is the right-hand side of the rule covering conclusion and perhaps the retract and assert definitions if necessary.
Rule Firing
The current values of all the attributes are specified with the contents of the knowledge-base (including current sensor readings, measurements, inputs examination, etc.).
From logical point of view it is a formula of the form:
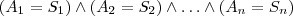 Eq: state-formula
where
Eq: state-formula
where
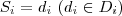 for simple attributes and
for simple attributes and
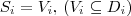 for complex.
for complex.
ANY and NULL
- In case the value of A_i is unspecified we shall write A_i = NULL (a database convention).
- Following a Prolog convention and logic, a ANY attribute value is possible in comparison (see
_in Prolog). - The semantics can be: „any value”, „not important”, etc.
- The solution:
- in preconditions, we can only use ANY, i.e. an atom such as
A=_can be specified, meaning „any value”, „all possible values of the attribute”, „we don't care” - on the other hand, attribute A unspecified, in the state formula means
A=NULL, so we store NULL in state - here we come to an inference rule:
A=NULL=⇒A=_. Seems to be valid… This rules should be optionally disabled/enabled in the inference engine.