The HeKatE Case Loan
Eliasz Kańtoch,
Tomasz Michalski
original by sradzik
Description
This is an example of a system which computes cutomer's credit rating. It takes into account a few parameters describing customer status and computes his status in two stages. Firstly it does a preliminary check using customer's base financial parameters and if he passes this test his financial status will be analyzed more thoroughly.
Conceptualization
Vocabulary
Customer - A loan debtor
Loan - A type of dept, a sum of money lent at interest
Credit rating - An estimate of the amount of credit that can be extended to a company or person without undue risk
Monthly income - Average value of customer's monthly income
Mortgage loan - A loan secured by a mortgage
Instalment - Amount of money payed back every month
Original Rules
Analysis
Examination of customer's credit rating begin with checking if his income multiplied by a certain coefficient is higher than his monthly instalments. Modeling this inequality in HeKatE methodology requires computing both sides of this inequality and comparing them in next table. If that condition is met, control should be passed to another system. Additional checks will be performed there, taking into account additional customer data.
Empty cells in decision table will not have influence on the final decision.
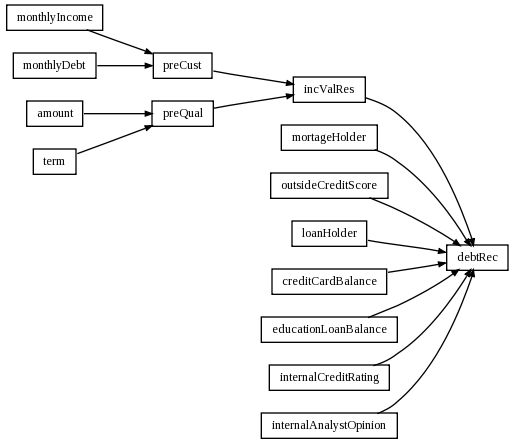
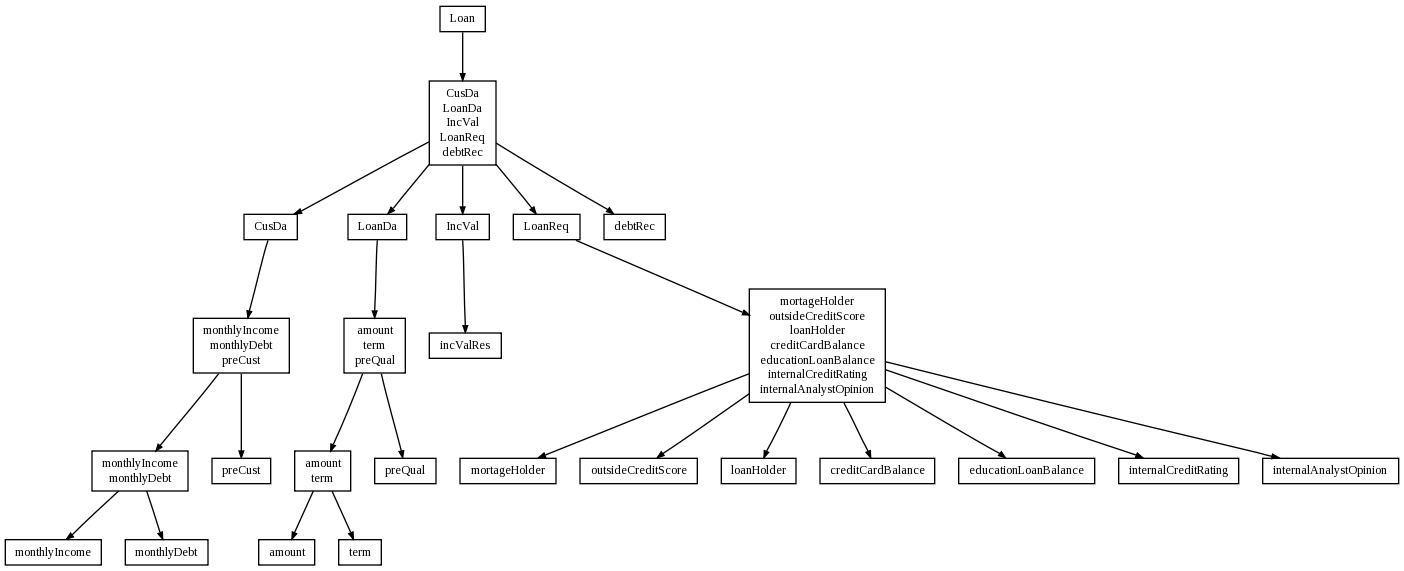
Conceptual model design starts with Loan attribute. It is finalized to four conceptual attributes and one phisical - debtRec. This attribute is system output (final credit rating).
On level 2 we can see that debtRec directly depends on IncVal and LoanReq. IncVal represents customer data needed to check inequality CusDa and loan data LoanDa. Attribute LoanReq contains informations necessary to final veryfication of customer's credit rading.
Level 3 and 4 finalizes all conceptual attributes together with all relations between them.
Comparing XTT table prototype with XTT logic model we can see some differences. Tables created from LoanDa and CusDa conceptual attributes were merged into one table. It happend because both tables were used to compute value of single inequality. Unfortunatelly there is no possibility to design ARD diagram in such way that there will be two attributes on action side.
Table, where both sides of inequality are compared was also modified. In order to compare two attributes one of them must be in table header, second - written in table cell with its operator.
Conceptual design
General Conceptual Design
Directed Conceptual Design
Full ARD Model
Diagrams design in VARADA:
loan-model.pl
The full hierarchical diagram is presented below:
ARD diagram:
TPH diagram:
The full hierarchical diagram generated by HQed:
Refined Conceptual Design
Physical Attribute Specification
| Name | Type | Scope | Comment |
| amount | float | [0; inf] | loan value |
| creditCardBalance | float | - | balance of credit card |
| debtRec | enumerate | {high; mid; low} | credit rating |
| educationLoanBalance | float | [0; inf] | balance of educational credit |
| incValRes | bool | {true; false} | result of preliminary check |
| internalAnalystOpinion | enumerate | {high; mid; low} | opinion of internal analyst |
| internalCreditRating | enumerate | {a; b; c; d; e; f} | internal customer's credit rating |
| loanHolder | bool | {true; false} | true if customer has other debts |
| monthlyDebt | float | - | current monthly instalment |
| montlyIncome | float | [0; inf] | monnthly income |
| mortageHolder | bool | {true; false} | true if customer has mortage |
| outsideCreditScore | integer | [100; 900] | external customer's credit rating |
| preCust | float | - | attribute necessary to compute inequality |
| preQual | float | - | attribute necessary to compute inequality |
| term | integer | [0; inf] | number of instalments |
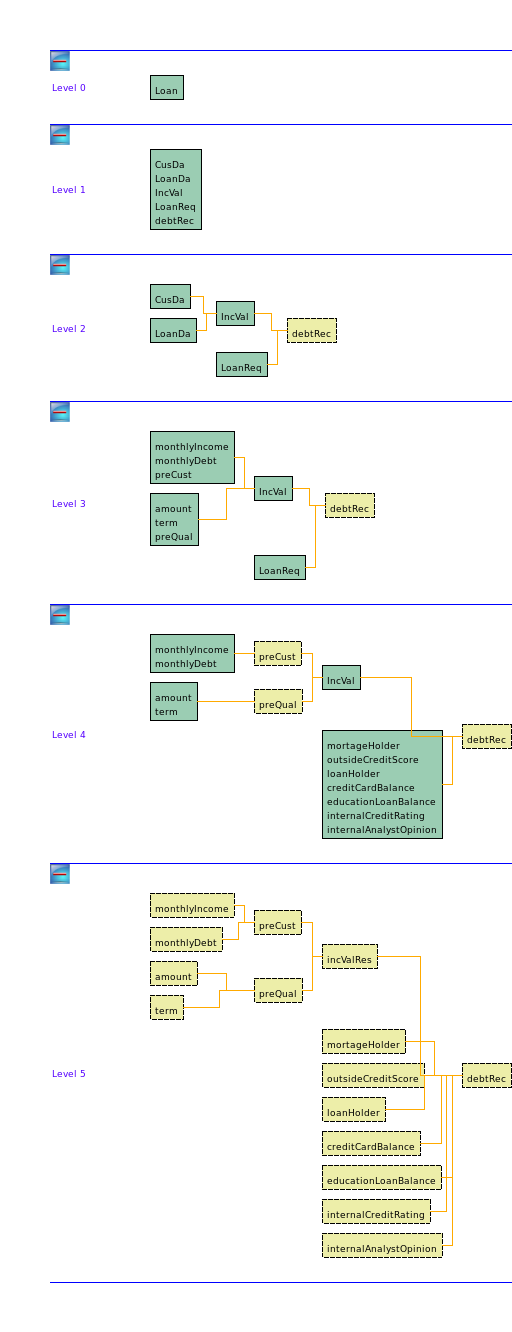
Structuralization
XTT diagram generated by VARDA:

Logical design

Design made by HQed
xttml model: